Review YOLOV10 (draft version)
Review YOLOV10
YOLOv10 is released in May 2024 by Tshinghua Researchers. I write a review article to see if it is the best YOLO ever.
History of YOLO
Redmon, the father of YOLO, implemented YOLO version 1 to 4 in C programming language using Darknet framework. Glenn Jocher, Founder and CEO of Ultralytics, rewrote YOLOv3 using Pytorch. Because Python is a flexible programming language, Glenn’s YOLOv3 is really easy to be trained and developped. In 2020, Ultralytics launched their YOLOv5. YOLOv5 has very strong community and it is well maintained by the Ultralytics developers. Later YOLOs such as Scaled-YOLOv4, YOLOv7, YOLOR, were developped based on YOLOv5 repo. Besides, there are YOLO self-developped by their authors. They are YOLOX, YOLOv6. Later, Glenn Jocher and his team in Ultralytics launched their next version of YOLO, YOLOv8, in 2023. In Febuary 2024, YOLOR’s authors released YOLOv9. In May 2024, researchers from Tshinghua University introduced YOLOv10, the latest YOLO so far, based on YOLOv8 architecture.
YOLOv8
Before investigating YOLOv10, let’s have a quick glance at YOLOv8. YOLOv8 is so far the latest YOLO proposed by Ultralytics. It was introduced to achieve high rate of accuracy measured by COCO and Roboflow100 benchmark across many tasks. YOLOv8 offers easy-to-use CLI and is organized in a well-structed Python package. What makes YOLOv8 a popular object detector is its large community. We can easy to find many well-written documents, tutorials, and applications on the Internet. Additionally, their developpers are really supportive and we can easily to get help if we encounter a problem.
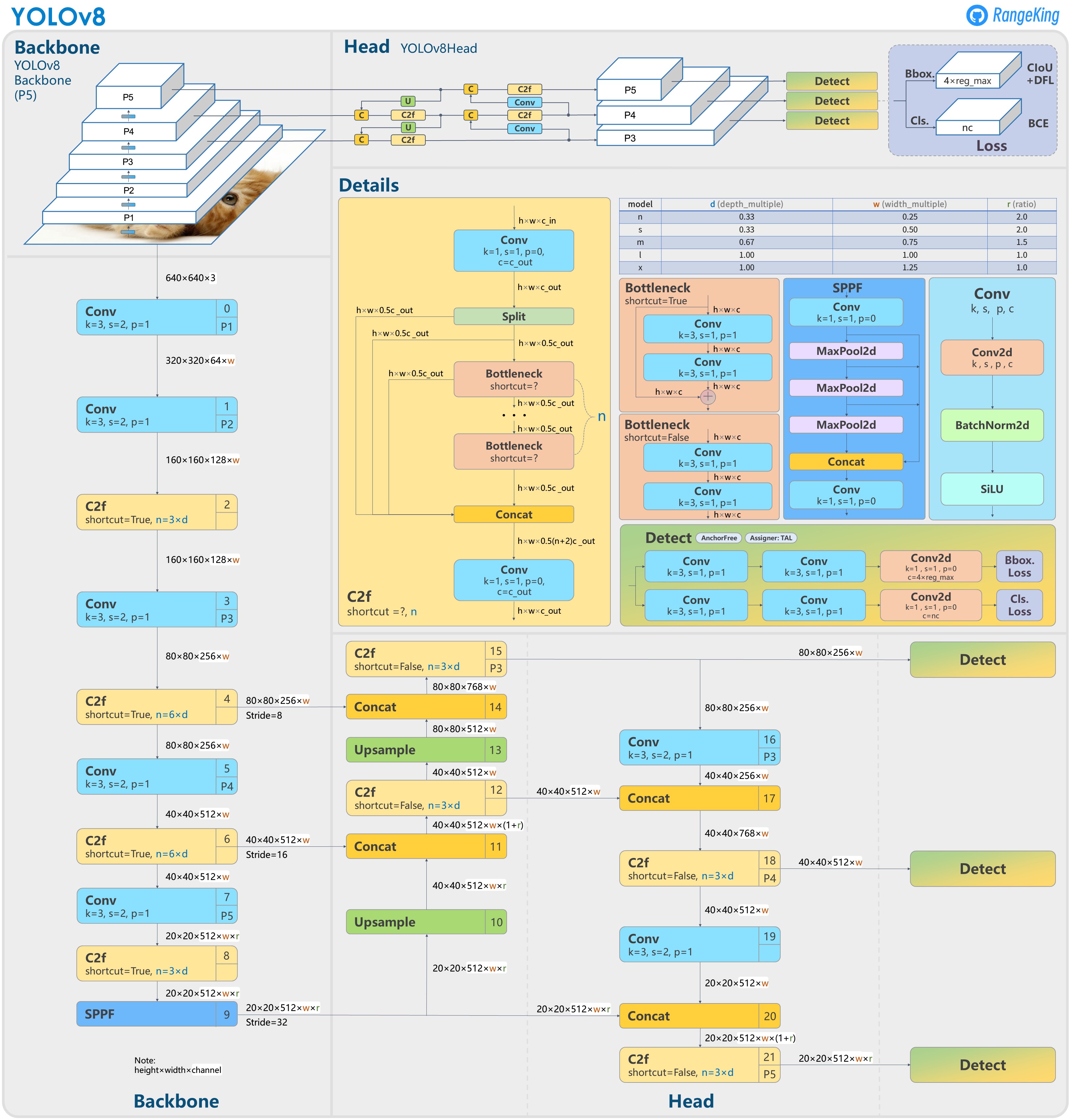
Compared to YOLOv5, YOLOv8 has some noticeable updates
-
YOLOv8 is anchor free. YOLOv8 removes anchor boxes because anchor boxes increase the number of box predictions, which leads to heavy NMS cost.
-
They introduced new convolution layer. The first convolution layer uses 3x3 kernel instead of 6x6 kernel. In CSPNet, they replace C3 by C2F implementation (C-CSPBlock, 2/3-Number of Bottleneck block, F-Fast implementation). Bottleneck block is just a fancy name of 2 convolution layers.
-
They turn off Mosaic Augmentation in the last 10 epochs.
Review Assigner and NMS
Assigner - Choose positive samples
Assigner is used while training object detector model. It used to pick the cell’s predictions that contributes to the loss function (a.k.a responsible for an instance/ground truth). Different models use different assigning strategies. Assigner chooses the positive samples based on IoU of the predictions and grouth truth.
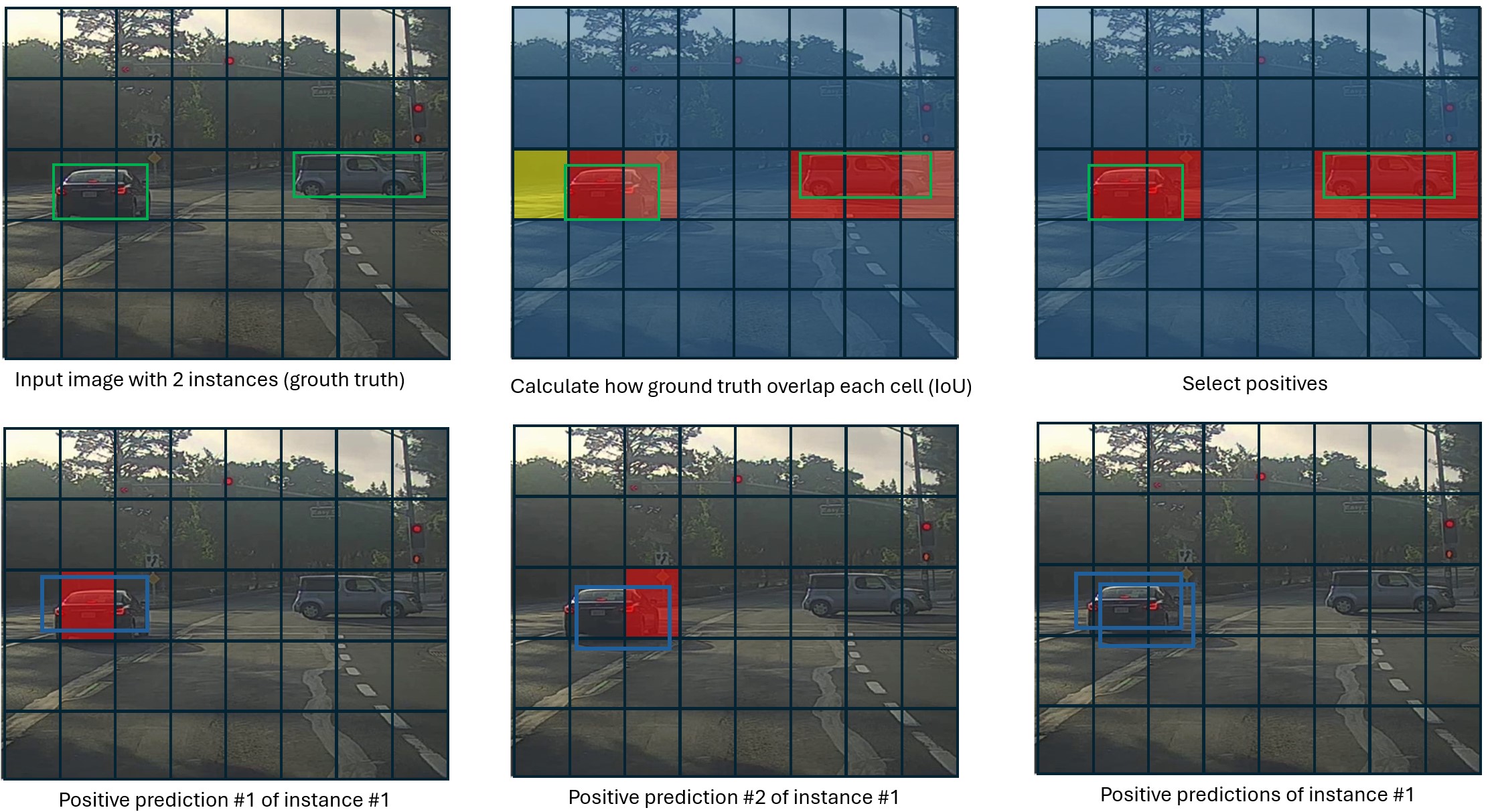

NMS - Non-maximum Surpression
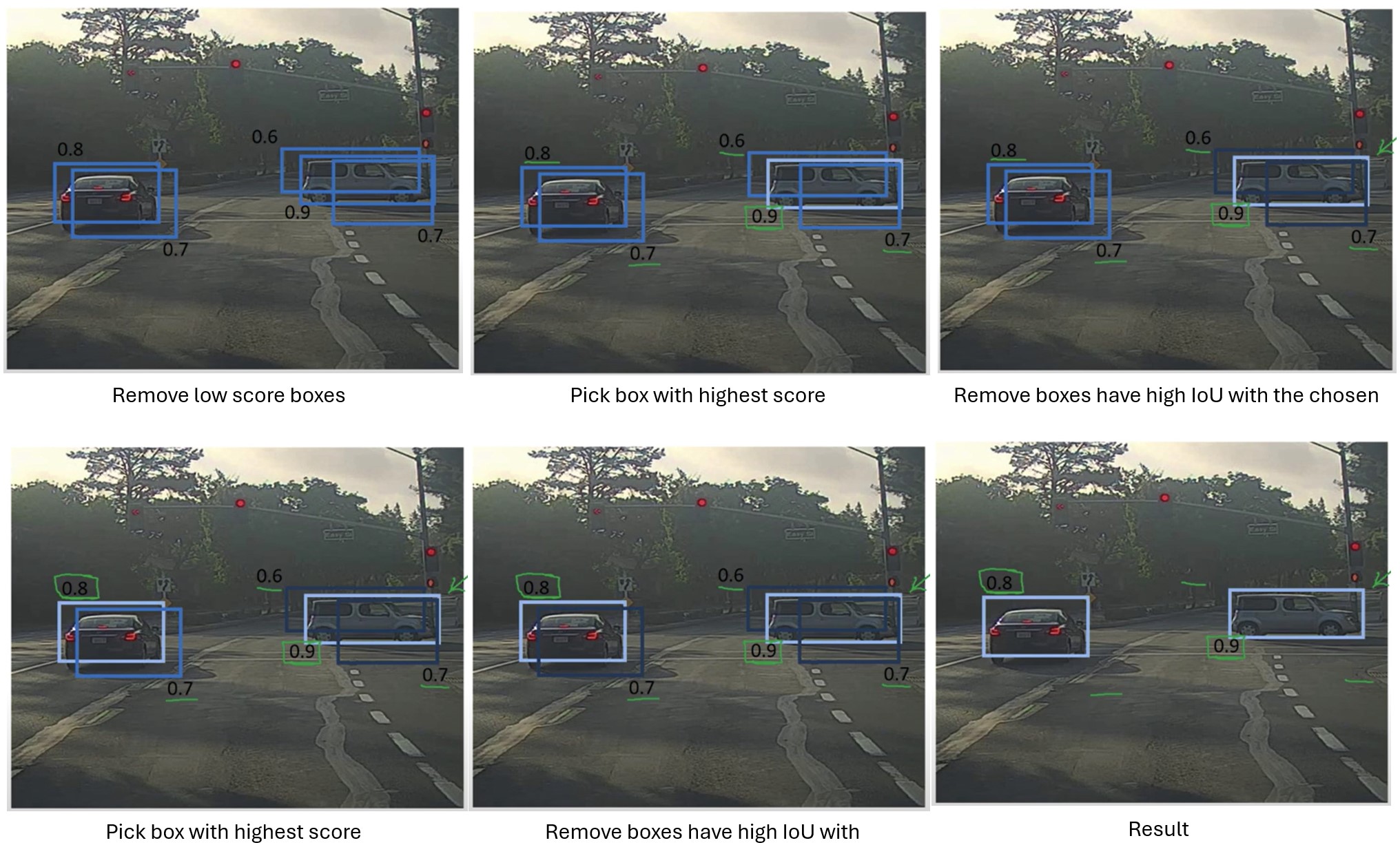
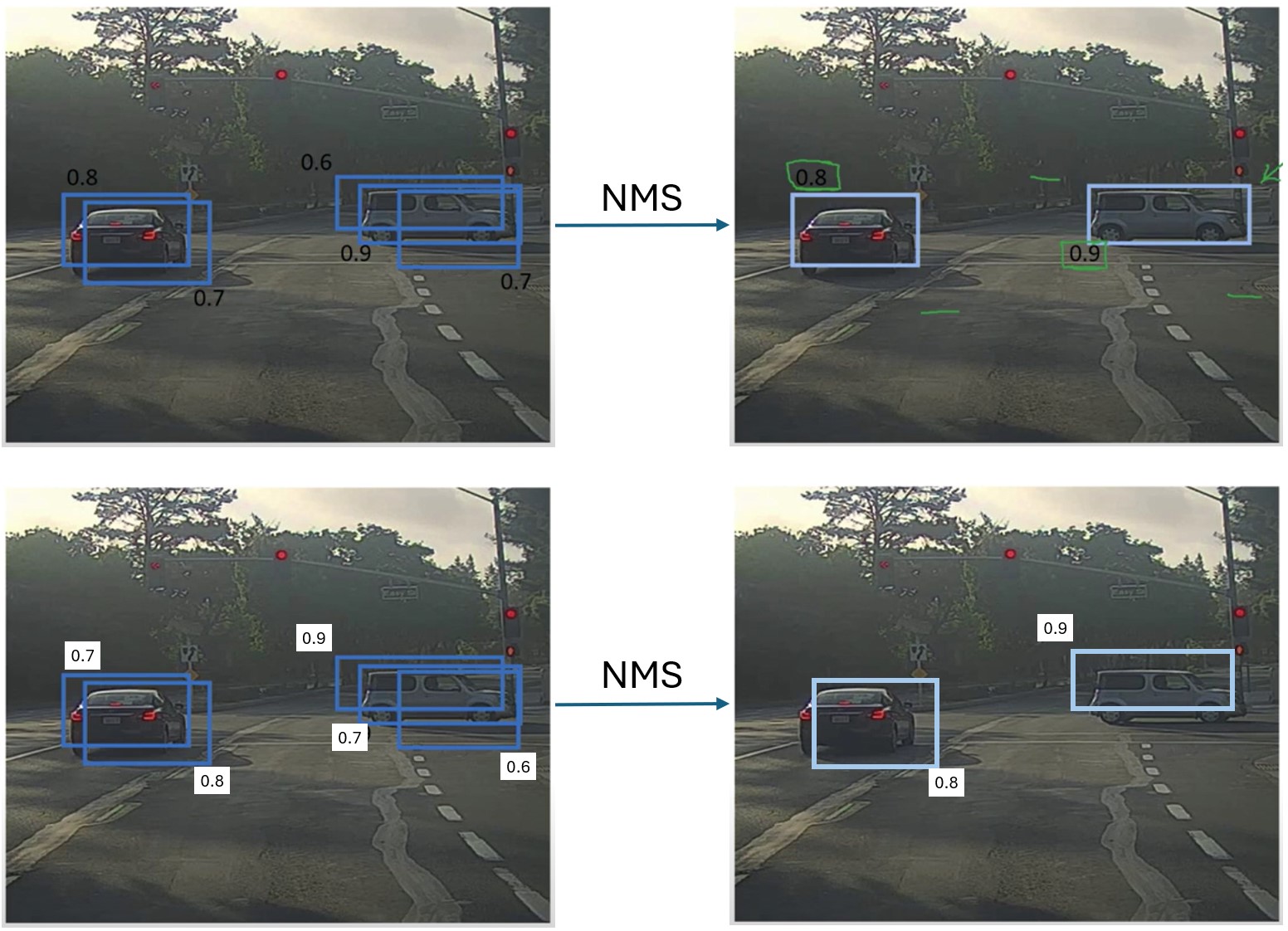
While Assigner is used in training process, NMS is used in postprocessing step of inference process. NMS chooses the box with highest classification score, and remove boxes having high IoU with the chosen one.

Misalignment between Classification and Localization task
The optimal anchors for classification and localization are often inconsistent, and may vary considerably depending on the shape and characteristics of the objects. The main reason is that the model performs 2 tasks using 2 separate branches without or lack interaction between them.

Task-aligner
Because using IoU or CLS score leads to task bias and then missalignment, a metric representing for both tasks of the object detector is necessary. The author of TOOD. Uses this metric to choose top 10 predictions for each instance. YOLO v6/v8/v9/e use task-align learning as Assigner.
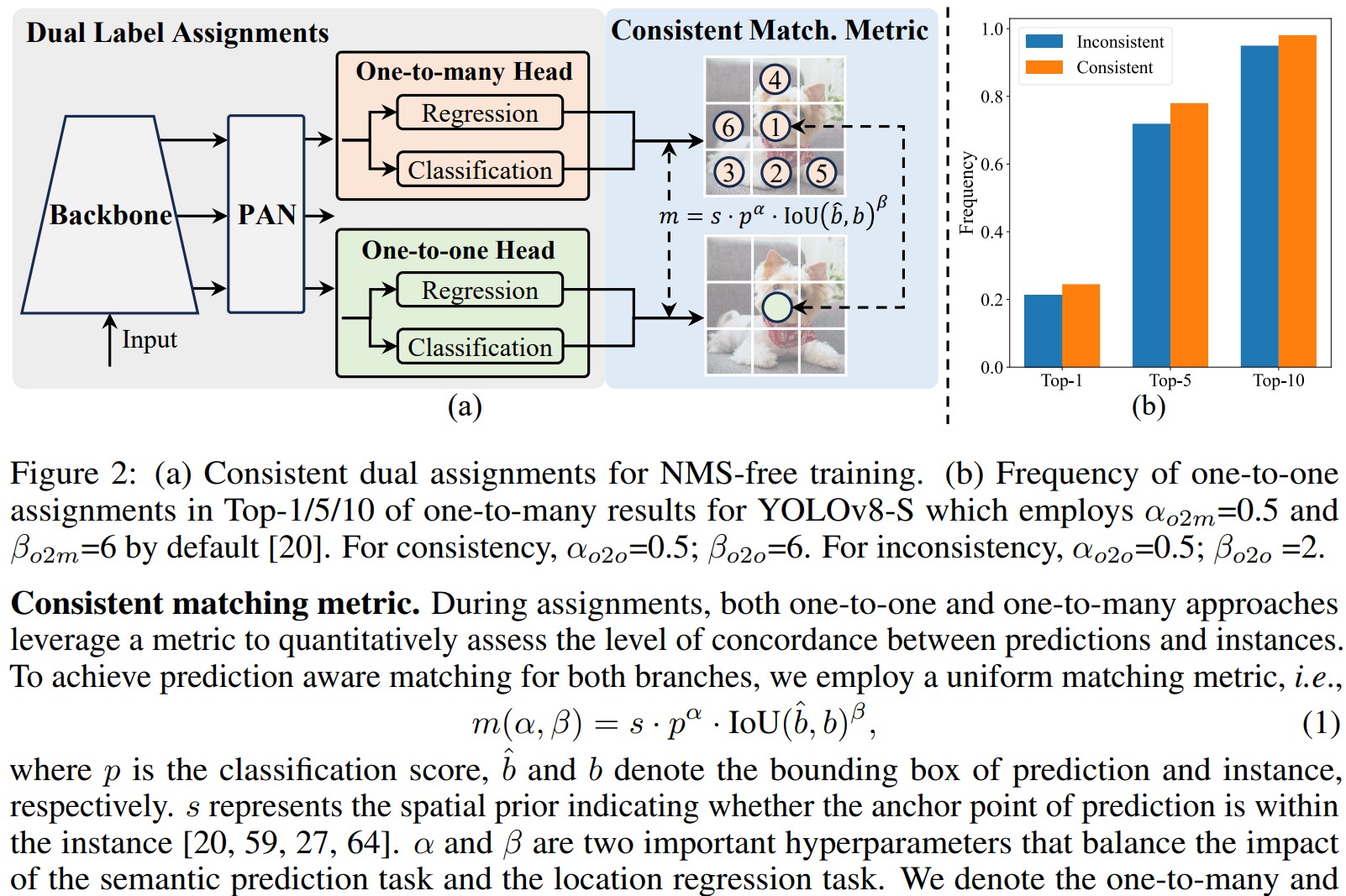
YOLOv10 removes NMS by Matching Metrics and Dual Label Assignment
YOLOv10 authors introduce a dual-head architecture. Particularly, beside the one-to-many head same as YOLOv8 detector, YOLOv8 has a one-to-one head that is identical to the one-to-many counterpart in term of structure.

YOLOv10 Model design
To compare the model architecture of YOLOv10 and YOLOv8, let’s take a look at their YAML configuration file in Ultralytics library.

Efficiency Improvement
Spatial-channel decoupled downsampling
Prior YOLOs perform spatial downsampling and channel transformation simultaneously using standard convolution layer with a kernel size of (3,3) and stride of 2. The shape (H,W,C) of the input feature map is transformed into a shape of (H/2,W/C,2C) of the output.
Compact rank-guided block
Deep stages and large models exhibit more redundancy. Consequently, using the same block design for all stages is suboptimal.
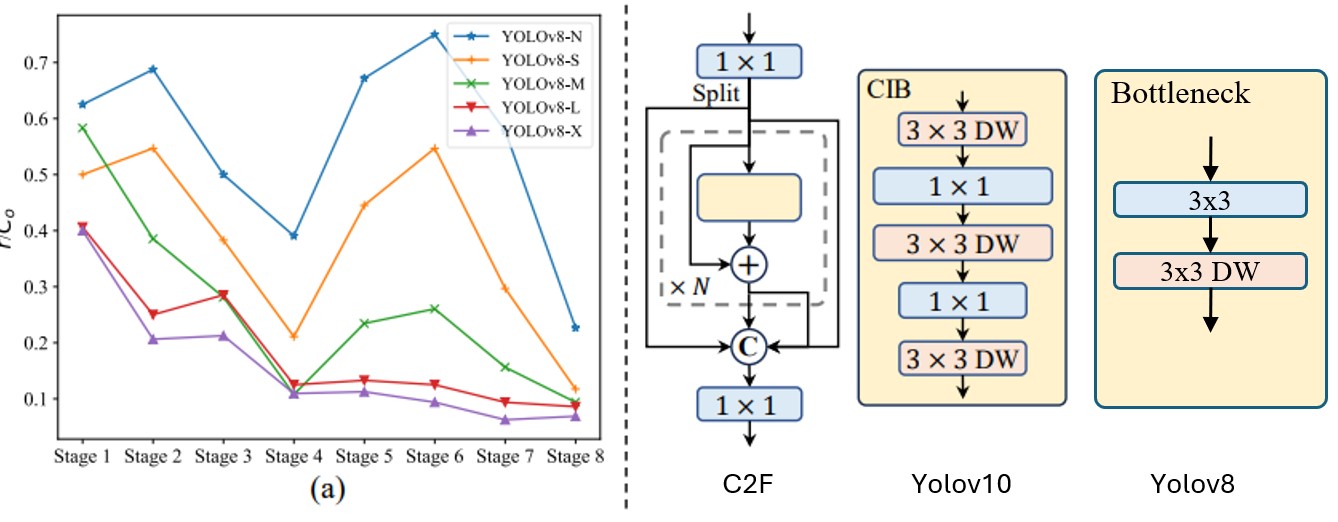
Accuracy Improvement
Using large kernel convolution
For small version of YOLOv10, they use large kernel size for first convolution layer in the network to enlarge the receptive fields.
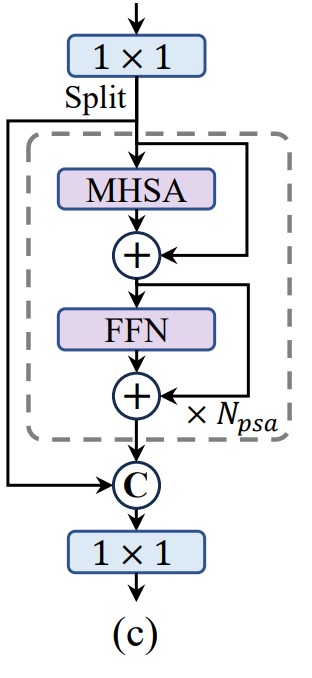
Partial Self-attention
Self-attention is widely used but it has high computational and memory cost. The authors propose PSA splitting features across channels into 2 parts: 1 part is performed self-attention, and then concatenated with the remaining part.